Diffusion and osmosis are two different types of inactive transport that play a vital role in transferring molecules in and out of the cell membrane. Many people can’t understand the differences between these two terms and consider them the same. However, there are many aspects that make diffusion and osmosis different from each other. This post will cover the dissimilarities between these two terms.

Table of Contents
What is diffusion?
The process that involves net movement from one point to another because of random kinetic activities of molecules or ions from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lesson concentration call diffusion. The movement continues until the state of dynamic equilibrium achieve. The process of diffusion is spontaneous, down the concentration gradient, and it is governed by laws of thermodynamics.
Types of diffusion Difference between osmosis and diffusion
There are two main types of diffusion.
- Simple diffusion
- facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion: In the process of simple diffusion, the solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution.
Facilitated diffusion: Facilitated diffusion is a kind of passive transport in which the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. The reason for passive transport is that the salute is moving down the concentration gradient.
Importance of diffusion
Diffusion occurs in both plants and animals and plays an important role.
Diffusion in plants
The process of diffusion is important to plant life; for example, the sugar in the cytosol take in by the mitochondria and destroys there; its concentration is always insufficient to mitochondria as referred close to chloroplasts, but the diffusion is a productive and rapid means of transport over very distance. However, it is not effective and rapid for long-distance transport.
Diffusion in animals Difference between osmosis and diffusion
In animals, diffusion is involved in the process of respiration. The important molecules in and out of cells are significant for the uptake of substances required by cells and also the removal of waste products produced by these cells.
What is osmosis?
The process Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules from a point of their higher concentration to a point of their lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane. The solvent in all biological systems is water.
Types of osmosis
There are two types of osmosis.
- Endosmosis
- Exosmosis
Endosmosis
In this process, the movement of water takes place inside the cell.
Exosmosis
The movement of water occurs outside the cells; when a cell place in a hypertonic solution, it shrinks.
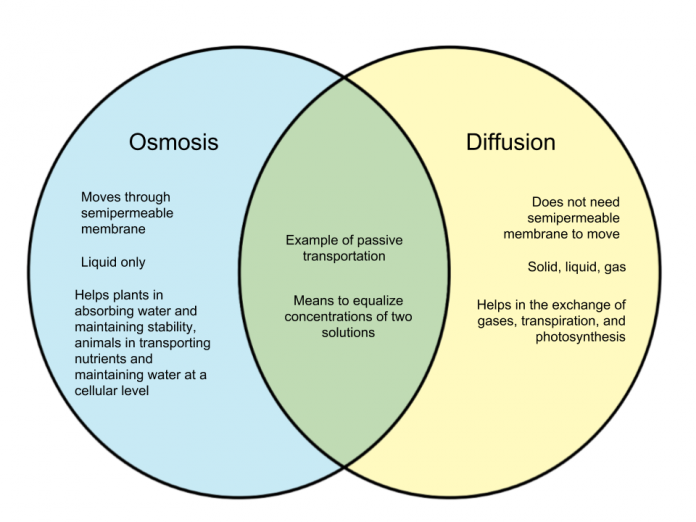
The main difference between osmosis and diffusion
- Osmosis limits only to the liquid medium, while diffusion occurs in liquid-solid and gas.
- The Osmosis needs a semipermeable membrane, while diffusion does not need a semipermeable membrane.
- Osmosis relies on the number of solute particles that dissolve in the solvent; on the other hand, diffusion depends on the presence of other particles.
- Osmosis needs water from the movement of particles, while in diffusion, it does not require water for the movement of particles.
- In osmosis, the flow of particles occurs only in a single direction, while in diffusion, the flow of particles occurs in all directions.
- Osmosis is not linked with the uptake of minerals and nutrients, while diffusion helps in the uptake of minerals and nutrients.
Also read: Difference between whose and who’s
Conclusion
Diffusion and osmosis are important in plants and animals. These two processes are passive transport, and both do not need any extra energy. Osmosis can only work in a liquid medium, but diffusion can occur in all mediums. The infusion of water in plants is an example of osmosis. Diffusion observes when a drop of any color adds to a glass of water. Eventually, the entire water content becomes colored.